The ideal when designing a product is to get the design right the first time, eliminating the need to make changes. However, changes due to wrong decisions and changes in customer requirements are unavoidable. If employees have made an undesired design decision, they need to manage product data in a controlled fashion using change management practices and approaches. This is the thought process behind engineering change management. We will also discuss change management best practices today.
In fact, employees can consider either of the 2 an engineering change or as a part of engineering change management;
- Alterations made in the functional, maintenance, performance, or physical characteristics of a product or a system
- Alterations made to a bill of materials by
- Adding or deleting an item
- Substituting an item with another
- Changing the usage of an item
This article aims to identify engineering change management best practices. But before we get into engineering change management practices let’s get to the preliminary lessons of IT change management best practices.
What is Engineering Change Management?
As markets accelerate, so does the pace of change. New technologies and evolving customer demands increase the pressure on engineering to make component adjustments to accommodate changes. They also need to maintain or improve efficiencies and profitability.
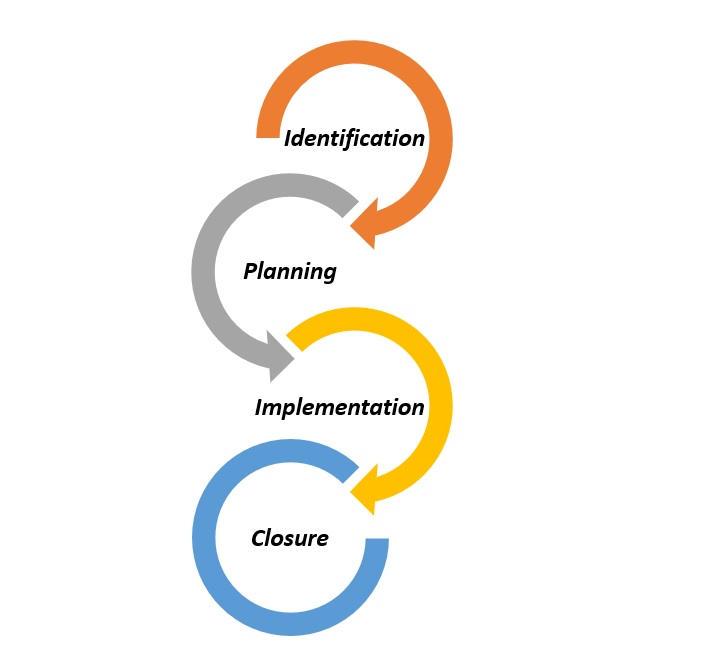
Engineering change management in the PLM system is a systematic approach to the documentation of changes from the identification of the required change, through the planning and implementation of the change, and culminating with the closure of the issue. All of this comes under the umbrella of engineering change management. Professionals looking to specialize in this field can benefit greatly from change management certification training, which equips them with the necessary skills and knowledge to handle such changes efficiently and drive successful outcomes.
Importance of Engineering Change Management
Engineering change management is all about forming, reviewing, and getting approvals and verifications for any modifications, engineering change requests, engineering change orders, and engineering change notifications. The process of engineering change management keeps a record of all the changes.
Engineering Change Management through a strategic and systematic process controls changes in product designs, processes, and associated documentation throughout their lifecycle. It ensures that modifications are carefully evaluated, approved, and implemented to maintain product quality, safety, and compliance. ECM involves assessing the impact of proposed changes, managing stakeholders’ expectations, and effectively communicating alterations to relevant parties. By streamlining this process, organizations can minimize disruptions, optimize resources, and enhance overall product performance and competitiveness.
By introducing Engineering Change Management, employees can
- For engineering change management, clearly indicate running change engineering or changes (preventing repetitive work going forward)
- Identify models and parts through engineering change management software that the change affects so the workflow incorporates the effect on other items
- Eliminate the use of paper routers and the inherent slowness of paper
- Increase visibility of progress, at any stage, to all workflow participants, as well as managers
- Ensure the most current versions of documents and drawings are in use
- Access revision histories easily through engineering change management software to permit understanding of the historical changes as well as create an electronic audit trail for review
- In engineering change management, permit changes to the workflow and associated schedule, with appropriate notifications so they can expedite the workflows and modify it to include new information, or just cancel
- Improve the accuracy of the workflow through engineering change management software by including more data (e.g., assembly and parts drawings) and the ability to markup and attach drawings and documents within the process.
Engineering Change Management Process
The engineering change process is at least a 4-step process that begins when a customer, manufacturing partner, or internal employee raises an issue or problem with a product. Then in the next part of engineering change management, manufacturers, operators, engineers, and others discuss the problem and determine the course of action. The group members then agree that a change is necessary. They then must agree upon a solution and then drive the implementation.
Engineering Change Request
In engineering change management, we will aim to identify engineering change request best practices but before that, we must understand its significance. Regardless of the scope of a change, and engineering change request, decision-making is the major part of any change, for this we need to look at the impact of the change, the costs, the risks involved, safety issues, short-term vs. long-term, and stop shipments. Engineering change request is also pivotal to any change.
Then there is the question of who gets to vote and what authority is needed on which type of change, for there are usually 3 types of changes in engineering change management:
Critical
If it is a change that has a big financial impact e.g., product recall, the top management needs to be involved and have authority over this
Major
In engineering change management, if the change affects the organization but to a certain amount of financial impact, the directors would have authority and their signoff would be required for such a change
Minor
A change that has minimum or no effect on functionality, is financially low impact does not require the top management or director’s signoff, and can be completed with the engineer’s or manager’s signoff only e.g. typos in printing
Engineering Change Notice
Engineering Change Notice in the engineering change management process communicates the details of an approved change to someone who needs to know about the change. It often authorizes a notice recipient to make a change to the design or process, which may include purchasing new materials.
A detailed description and an explanation of the change should be captured on the ECN or (engineering change notice) form in engineering change management. The form must contain the list of the items impacted and how to disposition each of them. It should also reference the approved ECO (engineering change order).
Engineering Change Order
An engineering change order (ECO) specifies either new product design details or proposed changes to existing products. ECOs provide a list of all the components, assemblies, and other documents that they affect. All key stakeholders (change control board or “CCB”) including engineers, quality and procurement experts, manufacturers, and external design teams or supply chain partners receive the engineering change order in many cases. Every CCB member is responsible for determining the impact of the change order. He must also determine whether he can implement the ECO as planned and on time. CCB members will approve or reject the change and once all CCB members approve ECO, then they will act on it. We must understand here engineering change order vs. Notice are different as the former follows a detailed process and documentation, whereas, the latter is not always formal like ECO.
Engineering Change Verification
This is usually the next step of the engineering change request process. Engineering Change Verification determines whether we were able to do what we told everyone to do, did we get what was expected? The change process could have been initiated to achieve financial benefits like Cost Reduction or improvements in Quality and the ECV is to verify whether the percentage results we hoped for are achieved or not. Engineering change management process is quite crucial at this stage.
Engineering Change Verification also determines whether this change can be reused, or if a part of this process is reusable. If the results of the change are not as expected, this can be done again.
The Engineering Change Management Workflow
This change management practice operates in a cyclic form. Each change has a lifecycle, from origination through completion. Engineering change workflow or practice is the process of moving a change along a path, from one lifecycle state to the next.
Roles in Engineering Change Management
Customer
In engineering change management customer is the role that requests a change due to problems encountered or new functionality requirements; this can be a person or an organizational entity and can be in or external to the company that will implement the change.
Project manager
When it comes to engineering change management PM is the owner of the project that the CHANGE REQUEST concerns. In some cases, there is a distinct change manager, who in that case takes on this role.
Change committee
Before getting to engineering change management process we must understand that in engineering change management process a committee decides whether a Change Request will be implemented or not. Sometimes project managers perform this task as well.
Change analyst
The change analyst is the person who plans and implements the change; Then, the project manager takes upon the planning component.
Engineering Change Management and PLM
The essence of product lifecycle management (PLM) is to engage with the life of your product throughout its entire lifecycle – from conceptualization to development, from prototype to production, through maintenance and ultimately obsolescence
Types of changes in PLM
ECR
An engineering change request tells the users to change certain items. ECR can be requested against any revision of an item
ECO
An engineering change order tells users that they need to make changes to specific items, and go ahead and do the work
MCO
A manufacturer change order tells users the changes need to be made to the manufacturing data of items
Stop Ships
A stop ship alerts users to stop shipping or using an item. Stop ships do not allow any redlining
Deviations
A deviation is used to deviate from a process or specification for a specific time period. Deviations do not allow any redlining
Components of a PLM Engineering Change
An engineering change process leads up to the critical event: an item (part or document) becomes formally accepted for its intended use. Agile PLM solutions then releases items using a change form commonly known as Engineering Change Notice (ECN) or Engineering Change Order (ECO). This Engineering Change Order otherwise known as ECO is a document that carries information on modifications that one must implement in the design of a product. Engineering change notice is a crucial segment of ECM.
When users approve the Change Form, it will change the release status of the affected item revisions from Pending to Released, or from Released to Canceled. Engineering change management occurs in PLM.
- A description of the problem encountered
- The reason there is a need for change
- A proposed change (optional)
- The part number(s) affected by the problem
- The part descriptions
- The request originator’s name
- The change request submission date
- The key stakeholders’ names and roles like change analyst, reviewers
- The disposition action required to resolve the original issue
Best Practices for Engineering Change Management
Change management could be tricky at times. The following are change management best practices to give you a perspective;
Unique Identifiers
On top of change management best practices this one holds significance. Each engineering change requires a unique identifier. It requires a manual identifier assignment process so that multiple requests don’t combine into a single order, or split a single request into multiple orders.
Change Number Source
For engineering change management, use a single identifier sequence for all change types. You’ll eliminate any confusion between, for instance, ECO 1234 and ECR 1234. Users can simply work with the change number without having to explicitly state the change type.
Proactive Change Management
Employees can make multiple changes in the product lifecycle where they are very inexpensive.
Incomplete but Accurate Product Design Data
Employees can do productive work on product and process definition information that is accurate but not complete. Retaining definition information until the design is complete reduces the enterprise’s agility.
Identify Owners Responsible for Changes to Data
All product and process definition information has owners who are responsible for understanding the impact of change on the data elements they own, these owners must understand how their data elements are related to other product definition information.
Owners as Approvers
Users or owners of the item undergoing change should approve. Also, managers should not necessarily be approving items every time.
More than 3 or 4 Approvers Typically not Required
Typically, once all key approvers sign off, other approvers should follow. And if employees need to know the change, they should use notifications.
Communicating Product Changes
Employees must communicate product changes throughout the enterprise and extend enterprise participants as required. Engineering change requests must follow a due process. And they should communicate the proposed and approved changes at the right time, to the right people.
The Holistic Approach to Change Management
You should take a holistic approach to change management. It further allows you to better understand the impact of change in all forms.
Conclusion
By implementing these best practices, organizations can navigate change efficiently, ensuring product quality, minimizing risks, and optimizing project outcomes in dynamic engineering environments.
If you require any further information or assistance regarding Engineering Change Management, change management best practices or Oracle’s Agile PLM, please get in touch with us at [email protected].
FAQs
Best practices include strong leadership support, clear communication, employee involvement, and progress monitoring.
An ECO should include a description of the change, reasons for the change, impact analysis, and approval signatures.
An ECR (Engineering Change Request) is a proposal, while an ECO (Engineering Change Order) is the approved change with implementation details.
Best engineering practices refer to established methods and standards for efficient and reliable engineering processes.

