Disasters can strike anytime, and companies need to have a robust disaster recovery plan to ensure business continuity. When it comes to Amazon Web Services AWS offers a range of disaster recovery architectures to help organizations build a resilient infrastructure that can withstand even the most severe disasters.
In this article, we’ll explore the best available disaster recovery architectures on AWS and how they can help companies maintain business continuity.
Why Plan for Disaster Recovery?
Take a moment to imagine a nightmare scenario where all the data in your production database is lost. What would you do? Would this spell the end of your business? Although you may have backups, have you ever tested them to ensure they work? How long would it take to recover all the lost data in production? How much data and revenue have you lost since the disaster occurred? Most importantly, what impact would this have on your customers and reputation?
If you’ve never considered these questions, it’s high time you do. Establishing a disaster recovery strategy systematically addresses these concerns and prepares for a disaster before it strikes. For startups and smaller enterprises lacking in-house technical leadership, leveraging CTO as a service can provide expert guidance in developing a robust disaster recovery strategy tailored to AWS infrastructure.
Disaster Recovery Plan
As part of your comprehensive risk management and business continuity strategy, evaluating the potential impact of an unlikely yet high-intensity event on your business is crucial. Many SaaS companies we work with have a significant responsibility towards their customers, particularly concerning data security and accessibility. If your business is in a similar situation, you must create a disaster recovery plan.
A Disaster Recovery plan should have the following objectives:
- Business Impact Analysis
Recovery Time Objective is the maximum time a business can tolerate for a service or system to be unavailable before the impact becomes unacceptable.
Recovery Point Objective is the maximum acceptable amount of data loss a business can tolerate during a disaster.
- Risk Assessment – performed to determine the likelihood of a disaster and the mitigation strategies you can implement.
Extent of Disaster Repercussions in AWS
Multi AZ Strategy
Within AWS architecture, each region comprises several Availability Zones (AZs), which, in turn, include one or more data centers in separate geographic locations. This design helps minimize the likelihood of a single incident affecting multiple AZs, reducing the potential impact of events like power outages, flooding, and other localized disruptions.
Employing a Multi-AZ DR strategy within an AWS Region can provide the necessary safeguards to withstand such incidents and ensure business continuity.
Multi-Region Strategy
AWS offers various resources to facilitate a multi-region approach for workloads. This approach ensures business continuity in an incident affecting multiple data centers in different locations.
This blog will primarily focus on multi-region strategies to illustrate disaster recovery strategies. However, these strategies also apply for Multi-Z and hybrid (on-premises workload/cloud recovery) approaches.
Architectures for DR Strategies and Implementation in AWS
Regarding disaster recovery (DR), we have a wide range of architecture options that businesses can use to build and implement effective AWS DR strategies. AWS’s DR solutions are designed to help businesses minimize downtime, reduce data loss, and maintain the resilience and availability of their IT infrastructure. Here we have a couple of best practices for implementing DR strategies in AWS infrastructure, including architecture options and key considerations of DR plans.
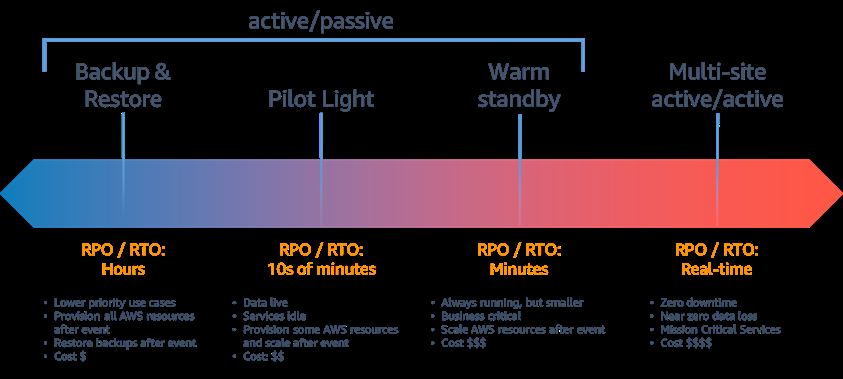
-
Backup and Restore
The backup and restore architecture is a basic disaster recovery strategy that involves regularly backing up data and restoring it in the event of a disaster. This architecture is suitable for companies with a relatively low tolerance for downtime, where data loss is acceptable.
AWS offers several services, including Amazon S3, Amazon EBS, and AWS Backup, that can help companies implement a backup and restore architecture.
The following diagram illustrates a Backup & Restore architecture that incorporates cross-region backup functionality:
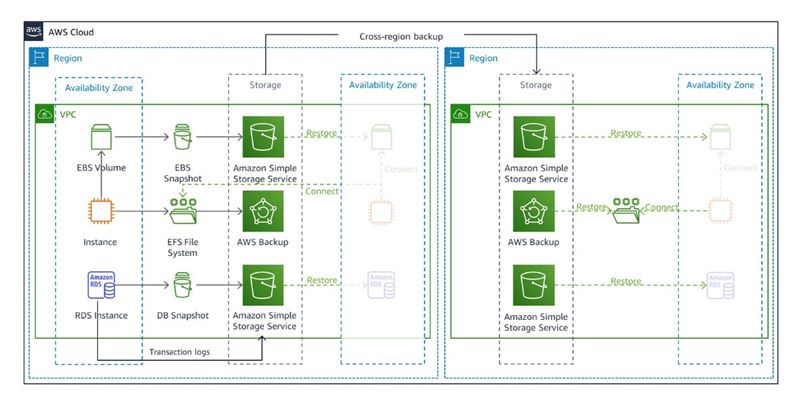
Figure 1: Backup & Restore DR Architecture (Source Amazon Docs)
Amazon S3 is a highly durable object storage service that provides scalable storage for data backup and archiving. It allows organizations to store and retrieve any amount of data from anywhere on the web, making it an excellent choice for backing up data in the AWS cloud.
Amazon EBS provides persistent block-level storage volumes for use with Amazon EC2 instances. It enables organizations to create point-in-time snapshots of their data volumes, which can be used to recover from disasters or to create new instances.
AWS Backup is a fully managed backup service that helps organizations centralize and automate data backups across AWS services.
-
Pilot Light
The Pilot Light architecture involves replicating critical data and services in a standby environment, ready to be activated in the event of a disaster. This architecture is suitable for companies with a moderate tolerance for downtime and data loss, as the standby environment can take some time to be fully operational.
AWS offers several services that can help companies implement a Pilot Light architecture, including Amazon ECS and EKS Amazon RDS, and Amazon S3.
The following diagram demonstrates a pilot light DR architecture:
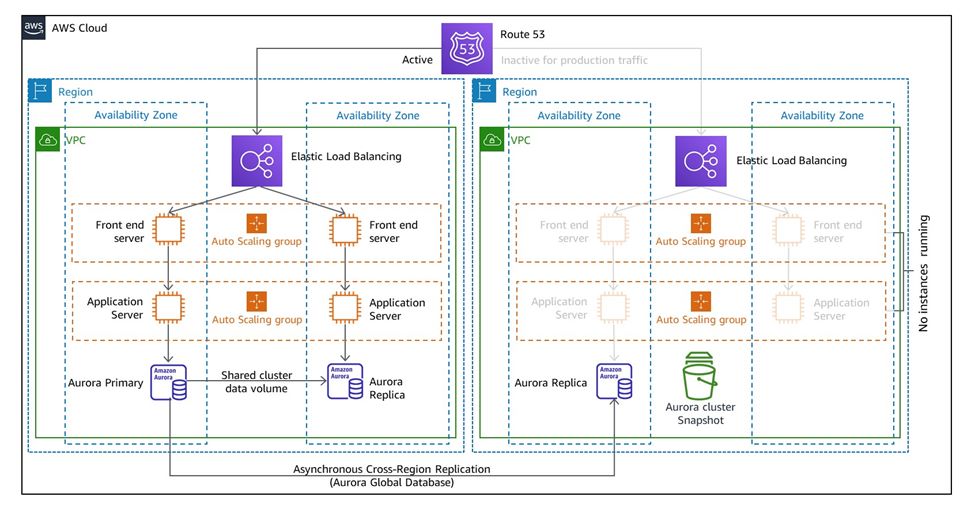
Figure 2: Pilot Light DR Architecture (Source Amazon Docs)
Amazon EC2 is a highly scalable computing service that allows organizations to launch and manage virtual machines in the cloud. It can be used to create a standby environment that can be quickly activated in the event of a disaster.
Amazon RDS is a managed database service that provides easy deployment, management, and scaling of relational databases. It can also replicate critical data in a standby environment, ready to be activated when needed. Amazon S3 can also replicate critical data in a standby environment.
-
Warm Standby & Hot Standby
The Warm Standby architecture involves replicating a significant portion of the production environment in a standby environment, ready to be activated in the event of a disaster. This architecture is suitable for companies with a moderate to high tolerance for downtime and data loss, as the standby environment can be quickly activated to minimize downtime.
AWS offers several services that can help companies implement a Warm Standby architecture, including Amazon EC2 Auto Scaling, Amazon RDS, and Amazon S3. Amazon EC2 Auto Scaling is a service that automatically scales Amazon EC2 instances to meet changing demands. You can use it to create a standby environment that can be quickly activated in the event of a disaster. Amazon RDS and Amazon S3 can also be used to replicate critical data in a standby environment.
 Figure 3: Warm Standby DR Architecture (Source Amazon Docs)
Figure 3: Warm Standby DR Architecture (Source Amazon Docs)
The Hot Standby architecture involves replicating the entire production environment in a standby environment, ready to be activated in the event of a disaster. This architecture is suitable for companies with a high tolerance for downtime and data loss, as the standby environment can be instantly activated to minimize downtime.
AWS offers several services that can help companies implement a Hot Standby architecture, including Amazon EC2 Auto Scaling, Amazon RDS, and Amazon S3. These Services can all replicate the entire production environment in a standby environment.
-
Multi-Region / Multi Sites (Active / Active)
The Multi-Region architecture involves replicating the entire production environment in multiple regions, ready to be activated in the event of a disaster. This architecture is suitable for companies with a very high tolerance for downtime and data loss, as it provides the highest level of resilience and availability. AWS offers several services that can help companies implement a multi-region architecture, including Amazon Route 53, Amazon S3 Cross-Region Replication, and AWS Global Accelerator.
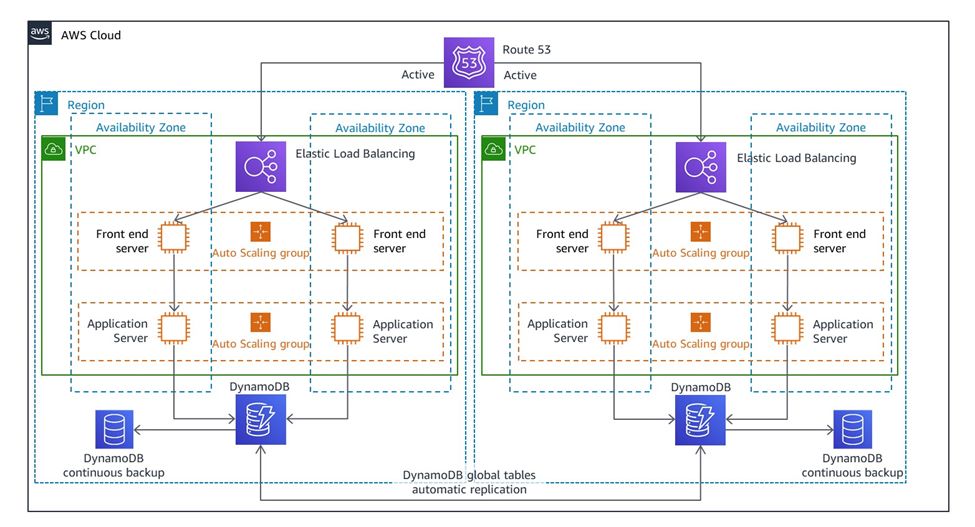
Figure 4: Multi-Site Active / Active DR Architecture (Source Amazon Docs)
Amazon Route 53 is a highly available and scalable cloud DNS service that you can use to route traffic between multiple regions. You can also use it to automatically redirect traffic to a standby environment in another region in the event of a disaster.
Amazon S3 Cross-Region Replication allows organizations to replicate data between different regions for disaster recovery purposes. AWS Global Accelerator is a service that improves the availability and performance of applications by using AWS’s global network infrastructure to route traffic to optimal endpoints.
Conclusion
In conclusion, there are several disaster recovery architectures available on AWS, each suited to different business needs and levels of resilience required. The choice of architecture depends on factors such as the tolerance for downtime and data loss, budget, and regulatory requirements.
By implementing a disaster recovery architecture on AWS, organizations can ensure business continuity and minimize the impact of disasters on their operations. With the right architecture in place, companies can rest assured that their critical data and services are protected and available at all times.
Do you want to know which AWS recovery architecture will work best for you? Drop us a line at [email protected] to book a FREE consultation session with our AWS-certified expert.

