In recent years, the shift toward microservices architecture has gained significant importance in the software development industry.
Microservices present several benefits compared to conventional monolithic applications, such as enhanced scalability, better isolation of faults, and quicker deployment cycles.
Conversion from monolith to microservices is a complex endeavour, but the benefits are worth the effort. In this article, we will explore how to convert monolith to microservices, the steps involved in the process, along with some examples.
What are Microservices-based Applications?
Microservices apps use a modern development approach in which a software application is built as a collection of small, independent, and loosely connected services.
These services are like small-software components. Each service works independently to perform a specific function. They communicate with each other through mechanisms such as APIs.
This approach contrasts with monolithic architecture, where the entire application is developed as a single unit.
Key features of microservices apps:
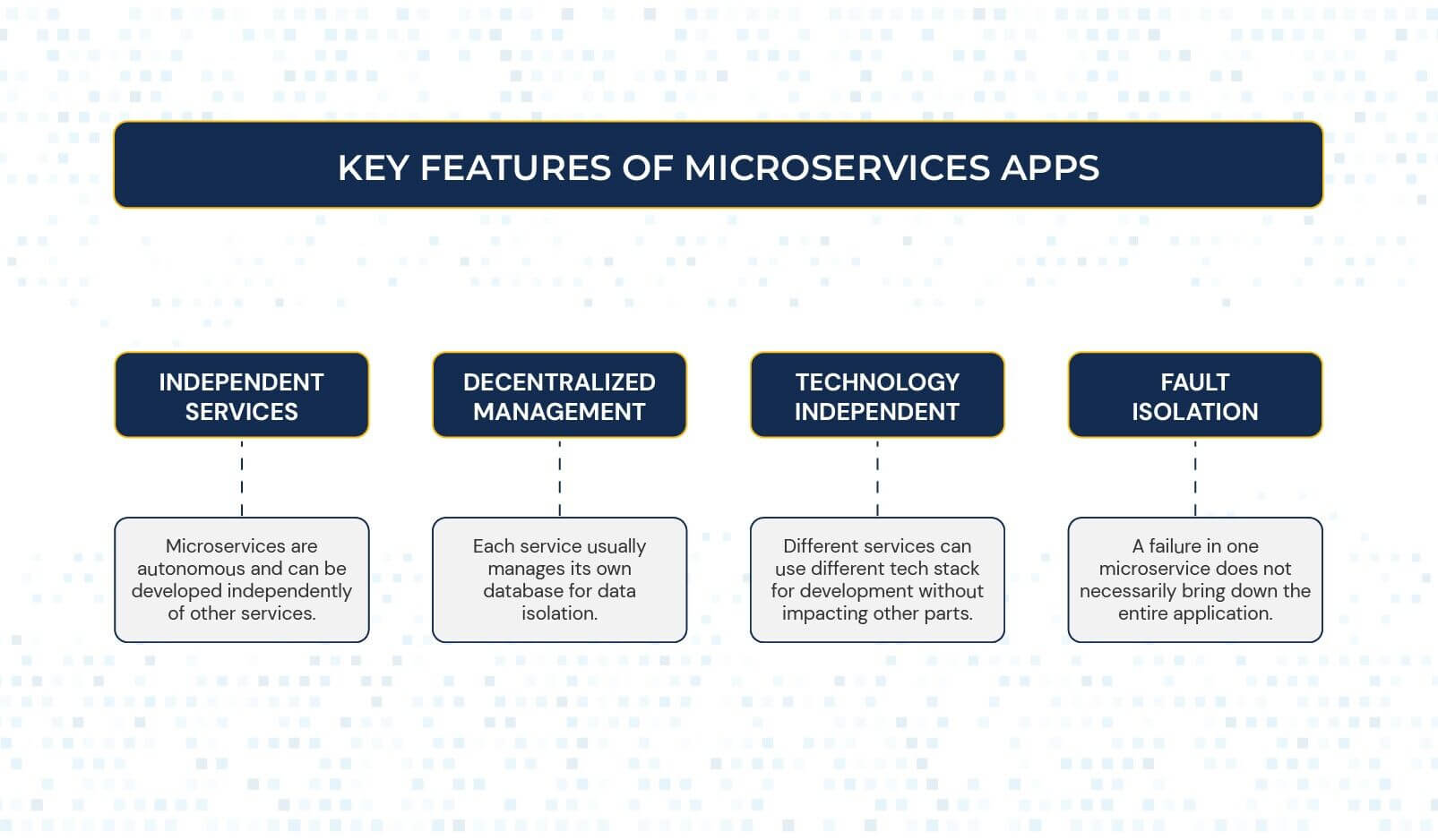
- Independent Services
Microservices are autonomous and can be developed independently of other services.
- Decentralized Management
Each service usually manages its own database for data isolation.
- Technology Independent
Different services can use different tech stack for development without impacting other parts.
- Fault Isolation
A failure in one microservice does not necessarily bring down the entire application.
Advantages of Monolithic App to Microservices Conversion
The reason why a company should switch to a microservices based architecture is due to the immense benefits it offers, not to mention that monolithic apps are fast becoming outdated.
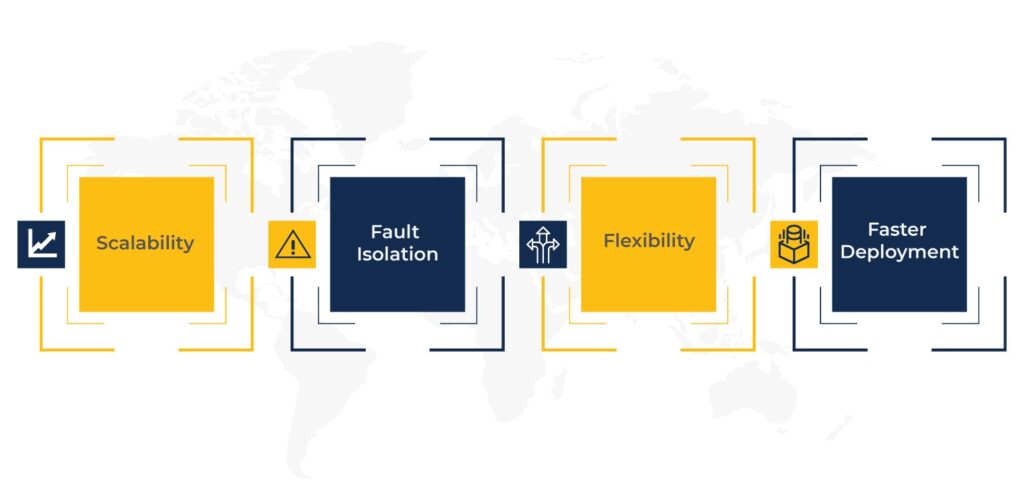
Here are some of the significant advantages of monolith to microservices conversion for your application.
-
Scalability
Microservices allow for horizontal scaling, meaning you can scale individual services independently based on demand. This enables better resource utilization and improved performance.
-
Fault Isolation
A major drawback of a monolithic application is that a problem in one of its components can bring down the entire app. But a microservices-based architecture isolates failures from specific services, ensuring that the rest of the system remains unaffected in case an application component is not functioning properly.
-
Flexibility
Microservices provide flexibility in technological choices. You can develop different services using various programming languages, frameworks, or databases based on specific requirements.
-
Faster Deployment
A microservices-based application enables faster deployment cycles since you can deploy each service independently. This allows for more frequent updates and feature releases.
Companies That Made the Switch: Monolithic Application to Microservices Examples
Here are some examples of companies that have converted their monolithic applications to microservices architectures.
- Netflix – Netflix used to have a monolithic application for its video streaming service. The application was difficult to scale and maintain, so Netflix converted it to a microservices architecture. This allowed Netflix to scale its video streaming service to meet the needs of its growing user base.
- Amazon – Amazon’s monolithic application for its e-commerce website made it very challenging to add new features. By converting it to a microservices architecture, Amazon was able to add new features to its application seamlessly.
- eBay –eBay struggled to maintain its monolithic application for its online marketplace. Therefore, the company decided to switch from monolithic to microservices, allowing it to improve the performance and reliability of its online marketplace.
Migrating from Monolith to Microservices: How to Convert Monolithic Application to Microservices
Converting a monolithic application into a microservices based architecture involves several steps. Let us look at the high-level process:
-
Planning and Assessment
Analyze the monolithic application and identify distinct business capabilities or functionalities your development team can decouple into individual services. Each service should have a clear purpose and be responsible for a specific task.
Pinpoint components of the app that can benefit from monolithic to microservices conversion. Define clear criteria for the migration process with a sequence wise migration plan.
-
Decomposition
This step breaks down the monolithic application into smaller, manageable component services based on each component’s functionality.
-
Define Service Boundaries
Determine the boundaries between the identified services. This involves understanding the dependencies and interactions between different components of the monolithic application and defining how they can be split into separate services.
Consider the following factors:
- Failure Isolation
- Data ownership
- Reusability
- Business functions
-
Refactor and Extract Services
Extract the identified services from the monolithic application, refactoring the code and separating the concerns. This step requires careful attention to ensure that each service is self-contained and has well-defined interfaces.
-
Technology Selection
The right technologies and frameworks are important for monolith to microservices migration. Consider following technical factors to determine the tech stack for microservices.
- Programming language
- Runtime environment
- Containerization platforms
- Orchestration tools
- Communication protocols
Make sure that you choose the tech stack that aligns with your business goals. The skill set of your team should also match the technology.
-
Establish Communication Mechanisms
Design and implement communication mechanisms between the services. You can achieve this through synchronous or asynchronous protocols, such as REST APIs, message queues, or event-driven architectures.
-
Data Management
Address the data layer by deciding how data will be managed across services. This may involve migrating to a microservices-friendly database or implementing data synchronization mechanisms.
-
Implement Service Orchestration
Define the overall flow and coordination of the services. This can be done using various approaches, including choreography or a centralized orchestration mechanism.
-
Implement Infrastructure and Deployment Automation
Set up the necessary infrastructure, such as containerization platforms or serverless environments, to support the deployment and management of microservices. Automate the deployment process to enable faster iterations and scaling.
-
Testing and Validation
Implement comprehensive testing strategies that simulate real-world conditions, such as:
- Unit Testing
- Integration Testing
- End-to-End Testing
- Performance Testing
In this way, microservices can identify and address potential failure scenarios.
-
Monitoring and Refinement
Monitor the performance of microservices to identify performance issues and errors. Feedback from users to gain insights into microservices helps resolve issues quickly.
Implement microservices in phases, starting with low-risk services and gradually increasing the scope. Continuously refine microservices to meet evolving business needs.
Tips for Efficient Monolith to Microservices Migration

Here are some of the best practices to efficiently convert monolithic app to microservices.
-
Understand Your Monolith App
Thoroughly analyze your existing monolithic application to identify dependencies and functions. Utilize specialized tools to map out the system accurately.
-
Identify Suitable Components
Choose components that are loosely coupled and have minimal dependencies, as they are easier to migrate without affecting overall performance.
-
Adopt an Incremental Approach
Adopt an incremental approach to refactoring that gradually replaces monolithic components with microservices without disrupting the entire system.
-
Implement CI/CD Workflows
Implement continuous integration and continuous deployment (CI/CD) pipelines to automate testing and deployment processes.
-
Security and Compliance
Incorporate security measures and compliance checks into the development lifecycle. This is vital to protect data integrity and adhere to regulatory requirements throughout the migration process.
-
Comprehensive Monitoring
Establish comprehensive monitoring practices to gain real-time insights into the performance and health of microservices.
-
Ensure Fault Tolerance
Design microservices with failure in mind. Implement strategies for failure handling and rapid recovery to maintain system resilience.
-
Evaluate and Improve
Continuously assess the performance of microservices. Make improvements based on feedback and changing requirements.
A Practical Conversion Example
Let us input the steps mentioned above in a practical example to illustrate the conversion process. Suppose we have a monolithic e-commerce application that handles user registration, product catalog management, and order processing.
Here is how the conversion might take place:
-
Identify Business Capabilities
Separate the user registration, product catalog, and order processing functionalities as individual services.
-
Define Service Boundaries
Determine the interactions and dependencies between the services. For example, the order processing service may need to communicate with the user registration service to validate customer information.
-
Refactor and Extract Services
Refactor the codebase, separating the user registration, product catalog, and order processing logic into separate services.
-
Establish Communication Mechanisms
Implement RESTful APIs or message queues to enable communication between the services. For example, the order processing service can make API calls to the user registration service for customer verification.
-
Data Management
Decide how data will be managed across services. It may involve replicating relevant data between services or adopting a distributed database solution.
-
Implement Service Orchestration
Define the overall flow and coordination of the services. For example, when a new order is received, the order processing service might trigger the user registration service to verify the customer’s information before processing the order.
-
Implement Infrastructure and Deployment Automation
Set up a containerization platform, such as Docker and Kubernetes, to deploy and manage the microservices. Automate the deployment process using CI/CD pipelines for faster iterations.
Conclusion
Converting a monolithic application into a microservices based application architecture is a complex process that requires careful planning and implementation.
Organizations can reap the benefits of scalable, high-performing apps by breaking down a monolithic application into smaller, loosely coupled services.
Although the monolith to microservices conversion process involves challenges and considerations, the long-term advantages make it a worthwhile endeavor for modernizing and future-proofing software systems in today’s dynamic and rapidly evolving technology landscape.
If you need assistance in converting your monolithic enterprise application to a microservices-based architecture, feel free to contact us at [email protected]. Our team will reach out to you and book you a free consultation session to see how we can help you.


