Suppose you are a fresh business graduate looking to work in the tech industry. You start applying to various companies for a job and visit technology sites and blogs to read and enhance your rudimentary tech knowledge.
You come across alien terms like React and MongoDB, microservices, Docker, and Kubernetes and you wonder what those terms even mean.
This article will dive into what microservices are, their history, benefits, and the latest trends in microservice architecture.
Let’s start.
When Did Microservices Start? A Brief History
Dr. Peter Rodgers coined the phrase “Micro-Web Services” during a 2005 conference on cloud computing. Rodgers argued that individual software components (services) can vary in complexity.
Therefore, any service, regardless of its complexity, can be made accessible to other services. To communicate these services, Rodgers suggested using something simple and familiar, such as a web address.
He compared this system to how Unix operating systems work, where small programs handle specific tasks and can be combined in flexible ways.
Thus, he established the basis of a functional microservice model for the first time. Based on his model, the term microservices debuted in software circles in 2011 and has since soared in popularity.
What is Monolith Architecture?
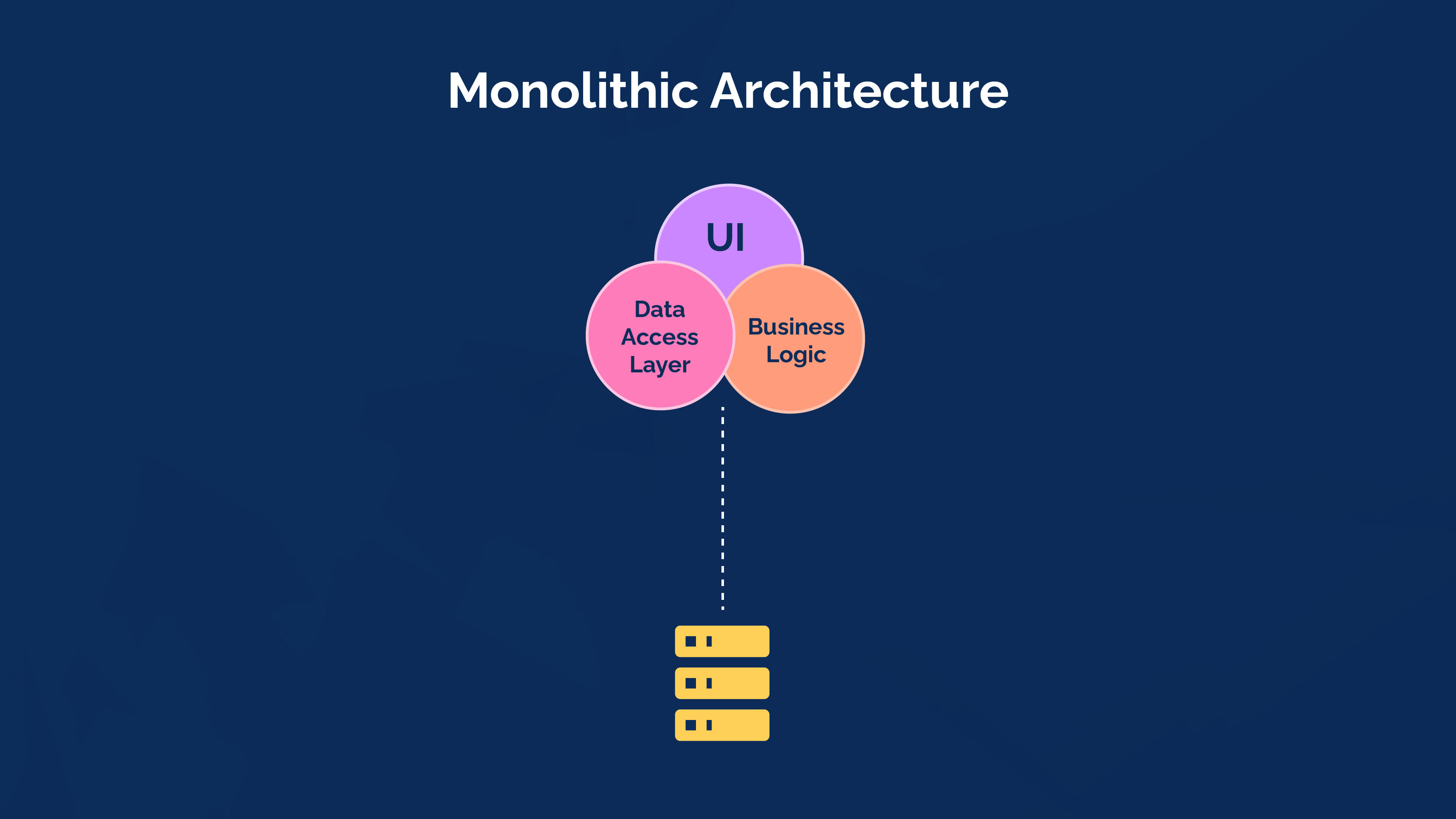
Before further discussing microservices, let’s talk about monolithic architecture. A monolithic program is large and has the application’s codebase consolidated in one location. It has some advantages, like requests not needing to make repeated calls across multiple networks.
And some disadvantages as well, including strong code coupling that makes it difficult to split individual capabilities into separate logic.
It is very challenging to operate monolithic applications on a single machine due to their enormous size and power requirements.
The technique of scaling up components of an application experiencing high workloads is called service architecture. It was formerly thought to be the solution to huge code bases.
Multiple operating system instances, each of which is capable of running a service, can be hosted on a single data server using the service architecture.
In a monolithic architecture, there are additional levels of infrastructure for engineers to handle, which results in hardware and server issues. Cloud Computing (Ec2), a web service released by Amazon, enables programmers to rent virtual machines inside Amazon’s data centers while Amazon takes care of hardware issues.
The virtual machine host, where the application’s code operates, is now the center of programmers’ attention.
However, this approach is ineffective because the code typically operates at or below its maximum capacity for virtual machines, making it very wasteful.
Containers, like Docker, are virtual machines that can conceivably be divided into several filesystem regions, each of which can house a program or a portion of an application in its own container.
The Evolution of Microservices
Microservices are containers of varying sizes, each providing its own functionality or service. It is an architectural approach employed in developing high-performance software.
The microservices architectural approach divides an application into smaller services, with each service using lightweight protocols like HTTP for communication.
The significant benefit of this approach is that it enables you to design and deploy application services independently of each other, thus making their management and maintenance more convenient and efficient.
Main principles of microservice applications
-
Multiple Components
As mentioned above, this modular approach is at the heart of microservices. A microservice architecture can be broken down into multiple interrelated components, each having its own purpose.
-
Business Oriented
In monolith architecture, the application is separated based on technological aspects, i.e., user interface and database. However, the different elements of a microservices application are usually divided according to their business function, such as:
- Inventory Management
- Customer Service
- Order Tracking
-
Decentralization
Microservices are autonomous and decentralized. If one of them stops working, the others can continue to operate normally as long as they don’t need to communicate with it.
This is made possible by every microservice having its own database and other essential components.
The Benefits For Businesses
Microservice architecture emerged as a solution to the limitations of monolith applications. This approach brought many advantages, prompting businesses to convert their applications to microservice architecture.
Here we have listed the most notable benefits of microservices:
-
Scalability
Scalability means that each microservice can be scaled according to the required load. In this way, businesses can make the best use of their resources and assign workloads accordingly, as some services handle more load than others.
-
Resilience
Since one microservice does not affect the other, microservice applications have great fault tolerance. Due to this isolation, the app’s overall functionality is less prone to specific faults.
Hence, businesses can ensure that their operations run normally even if there is a bug or error in one specific function.
-
Flexibility
Microservices are developed separately by the technical staff. This allows developers to choose the most appropriate tech stack for developing each service. As a result, developers are not bound by any particular technology or vendor and can deliver their best product.
-
Faster Development
Developers simultaneously work on different microservices, which significantly reduces the development time. Thus, businesses can bring their product faster in the market which can give them an advantage over competitors.
The Future of Microservices: Microservices Trends in 2025
The evolution of microservices is an ongoing process. There are several trends and technologies that will drive its future.
Major trends in microservice architecture in 2025
-
Kubernetes
Every solution seeks to address a unique set of issues. Disorganization followed the inevitable emergence of containers. The management of thousands of microservices simultaneously is quite challenging, which is why Google developed the open-source Kubernetes project.
Engineers may consolidate their containers with Kubernetes and make these services portable. The clusters of these centralized containers, known as Kubernetes, power the application.
Clusters group all necessary services and the application’s dependencies. This makes it relatively simple to transport, manage, and scale applications.
Containers can run simultaneously on several machines thanks to the Kubernetes clusters. This is highly advantageous for businesses that host massive volumes of data.
Google is an apt illustration of a business employing Kubernetes. Google simultaneously launches numerous versions of any one of its applications, including YouTube.
Each instance, which is a running instance of an application in a cluster, is also known as a pod. To ensure continuous uptime, Google updates YouTube one individual YouTube pod at a time.
-
Docker
So, where does Docker fit into all of this, then? Engineers can create and deploy apps inside packed files inside containers using Docker. These are the same containers that successfully deploy applications of the same version on any computer. Now you can see the combination of Docker and Kubernetes also.
Docker and Kubernetes complement one another to distribute containerized apps. With the help of Kubernetes, docker-created containers are organized into pods and run according to the machine’s resources or the needs of each individual container.
The scalability of applications has improved considerably due to the influx of users and data. Engineers only need to add extra containers to the Kubernetes clusters.
Both Kubernetes and Docker are unfinished tools that work together to build and manage large-scale applications; they are not distinct solutions.
-
Serverless Microservices
Microservices are increasingly becoming the preferred deployment method for serverless applications. With serverless microservices, developers can write code without the underlying system. This gives developers much freedom.
Serverless microservices will lead to applications that are easily scalable and faster to develop.
-
Service Mesh
A service mesh manages how services communicate with each other. It is a special layer that ensures safe and reliable interactions.
Additionally, service meshes also improve the safety of microservices, which is a boon for complex environments.
Separating the communication logic from the code allows developers to focus on their core tasks and not worry about infrastructure problems.
Conclusion
Today, most software development companies use the microservices architectural approach due to its incredible benefits. Given the breakneck speed at which technology is evolving, the need to scale and update applications has increased tremendously.
Microservices enable you to quickly meet the changes in customer demands and changing market dynamics.
As the microservices architectural approach gains popularity, it might even overtake traditional development methods in the future.
If you want to know more about Xavor’s microservices application development services, contact us at [email protected].

